// Thought ahead
When it comes to building a network, the software that is used is essential. There are many different technologies to choose from, and depending on the needs of the business, they can be useful and appropriate. Nowadays, SD-WAN, i.e. software-defined WAN, is often talked about when it comes to flexible site networking. But here, too, there are a wide variety of solutions and providers.
We are particular experts in the field of “Session Smart Routing” technology from Junipers 128 Technology – more info on the visionary technology here – as we have been on board practically from the very beginning and today operate the most complex SSR network structure in the world. But we are also familiar with other solutions such as viptela, Fortinet and others and can upgrade your existing network and extend it with work-saving and securing functions and services.



However, the innovation of a software is only one side of the coin. A productive use including effective tools, interfaces and functions the other. Over the years, we have worked closely with the relevant software vendors to develop numerous enhancements to make a groundbreaking piece of software even better.
Our add-ons increase both functionality and productivity within a company. All developments have been made with the aim of optimizing networks and automating processes. This enables us to react to extensive customer scenarios and offer completely individual solutions.
We make your network faster, more secure, more flexible – better!
We have prepared something
Our extensions
In the following we have collected our add-ons and explain briefly which functionality is behind each of them and in which exemplary use case each add-on can be used.
Ethernet over SSR
With the help of Layer2 Connections (ISO/OSI layer model) spatially separated networks can be connected directly via SSR (Session Smart Routing) without using different IP network areas. Both sides are part of the same network segment.
This means that the data does not have to be routed to the other side. The devices on both sides can communicate directly with each other. This is helpful if – as with classic routing – necessary techniques such as NAT (Network Address Translation) are to be prevented. With this technology, for example, local devices such as printers in a home office environment can be integrated into a company network without additional effort.
region-based routing
The packet flow (routing) can be influenced by a wide variety of characteristics. In region-based routing, these decisions are made based on location-based information. This enables certain data packets to be routed directly, i.e. by the shortest route, to their destination, whereas other packets are deliberately routed via other routes, for example to bypass bottlenecks or other obstacles.
This is particularly helpful if certain services are not available in a region and therefore the direct route is not possible.
WireGuard
With the help of the extension, the Session Smart Router can be quickly and easily supplemented with the modern and extremely high-performance VPN solution WireGuard. The centrally managed extension turns any router on a network into a dial-in point for VPN clients. External employees can thus have extremely simple and flexible direct access to the data they need. A complex routing is almost completely omitted here. The simultaneous use of several WireGuard connections can also be implemented here without any problems.
UTM/NGFW
The UTM (Unified Threat Management) feature adds the functionality of a classic UTM firewall to the Session Smart router, but combines it with SSR‘s revolutionary approach to routing. In contrast to classic solutions, this combination allows the data stream to be controlled and visualized much more efficiently and precisely. However, the protective functions are not only retained in full, they are even significantly increased by the integrated “zero trust” approach of the SSR routers.
Proxy
The service function chaining integrated in SSR allows individually defined data streams to be flexibly rerouted. This allows the use of any proxy solutions (e.g. Squid), with which the data can be accelerated, analyzed or filtered, among other things. The necessary proxy software is centrally managed and automatically made available on the respective router.
DNS filter
A first and easy to implement protection against internet based malicious code is the use of a DNS filter. The aim is to prevent unwanted websites (advertising sites, malicious code, etc.) from being called up.
This extension adds such a DNS filter to the Session Smart Router.
Innovative SD-WAN solution
Juniper’s Session Smart Routing
Juniper’s 128 Technology has taken on the task of developing a completely rethought routing software that not only replaces today’s network technology, but takes it to a new level. But how does it all work?
The setup of a network based on Session Smart Routing looks at first like common VPNs of today. Two sites use the Internet as a transport medium and an SSR router is used between the Internet and each site to encrypt and decrypt the data. The routers can be used in any network topology and replace your old, inflexible routers and firewall installations.
Instead of reading on, you can also watch our video on SSR. But beware: it gets technical!

Advantages
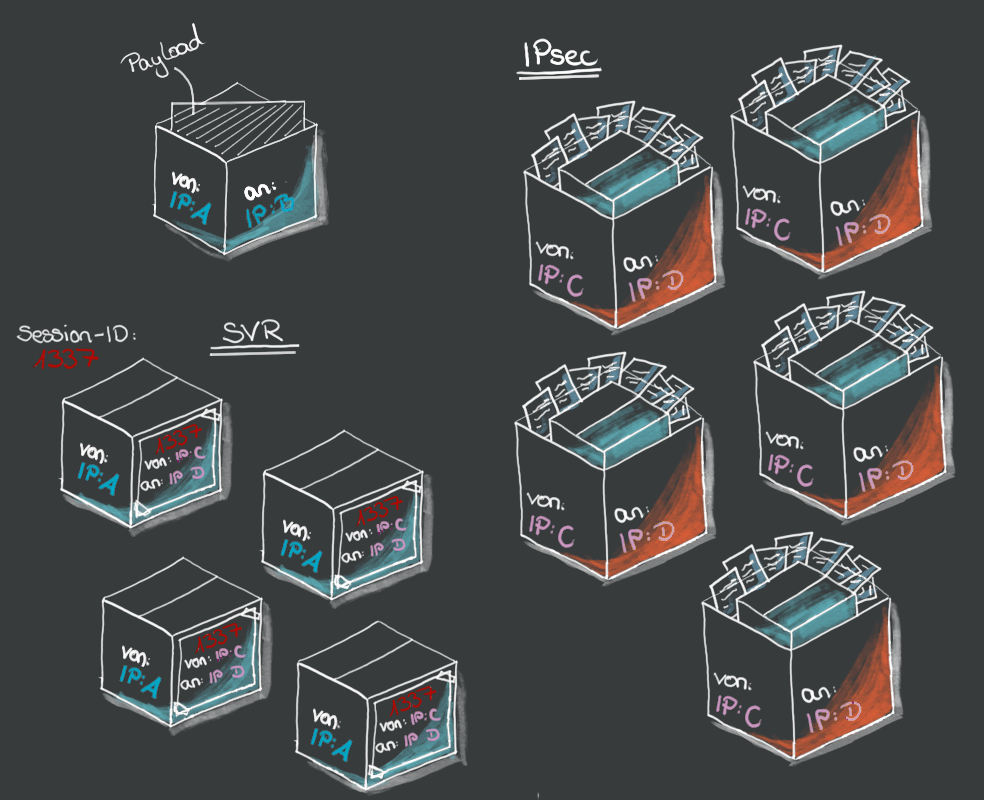
Less overhead
The main advantage of SSR is that the additional information that each individual data packet receives during transmission is significantly smaller. For secure sending, the packages must of course be encrypted. Unlike IPSec, for example (where all data is sent through a tunnel), SSR works with so-called sessions. A session with a unique session ID is created for each data transmission. Only the first packet of a session is then supplemented by the important metadata such as sequence numbers, security parameters or authenticity data and all further packets only receive the session ID as additional info. This saves me up to 30% overhead compared to the IPSec protocol. This leaves more space in each packet for the payload (the actual data to be sent) and I need fewer packets overall for a transmission.
Prioritization
Another great advantage of SVR is the ability to prioritize. This way I can give each packet an additional “label” that specifies the importance of this data transmission. This makes it possible to define precisely which applications have priority in data traffic and, in the event of a disruption, only less important data transmissions are delayed. This prioritization is not easily possible with IPSec.

Multi-line management
With SSR we have the decisive advantage that for the first time we can use several lines in parallel. This is also not possible with IPSec. All connections to an endpoint can only be sent via the line over which the current tunnel is established. In the event of a fault, a new tunnel must first be set up and it is not possible to switch over without further ado.
Thanks to SSR, on the other hand, the individual sessions can be distributed over several connected lines as required and, in the event of a fault, the session is simply moved to the next free line.
Example: We’re in the middle of a video conference and there’s a network glitch. If I use IPSec, the connection would simply drop, whereas with SSR the transmission continues almost without interference, as it is automatically redirected to another available line.
Flexibility
Juniper’s 128T technology is designed to be flexible so that new sites can be easily and quickly integrated into the network. The entire network is controlled and configured via the so-called Conductor. Settings and sessions can be created globally and transferred to each site, whereas with IPSec, new tunnels must first be set up with a great deal of effort.
Monitoring
Our claim is to provide you with fail-safe systems to ensure trouble-free operation. Through extensive monitoring, which means up to 3500 tests on a permanent basis, we can eliminate faults even before they become noticeable to you. We always keep an eye on jitter and latency and can therefore react to bottlenecks even before they occur, for example by rerouting the data traffic to another free line (multi-line management).